Digital Citizenship: Meaning and Definition

Eloise is a UK based primary educator and freelance writer. Passionate about education, she enjoys crafting engaging learning content.

George is an international school teacher based in Asia. A passionate language learner and polyglot, he thrives in diverse classrooms.
Digital Citizenship: Meaning and Definition
As young children increasingly use the internet and connected technologies, it is now essential for all primary school students to understand digital citizenship.
Previously, digital citizenship might have occupied a minor place in a schools overall learning provision, but it is now crucial for schools to clearly define digital citizenship for their students and provide them with straightforward, actionable strategies for being safe, responsible, and ethical online.
Incorporating digital citizenship into a comprehensive PSHE curriculum ensures that primary school children are equipped with the necessary skills to successfully navigate the online world and recognize when they or someone else are not upholding good digital citizenship practices.
What Does Digital Citizenship Mean?
Being a digital citizen means to positively engage with online technologies and communities in a safe, respectful and ethical manner. Digital citizenship goes much further than just staying safe online. While internet safety is highly important, being a digital citizen also entails using technology responsibly.
Teaching children to be responsible digital citizens is now more important than ever. With children accessing technology at younger ages and the role of technology continually evolving, students must understand the significance of being good digital citizens to prepare for the modern world and life beyond education.
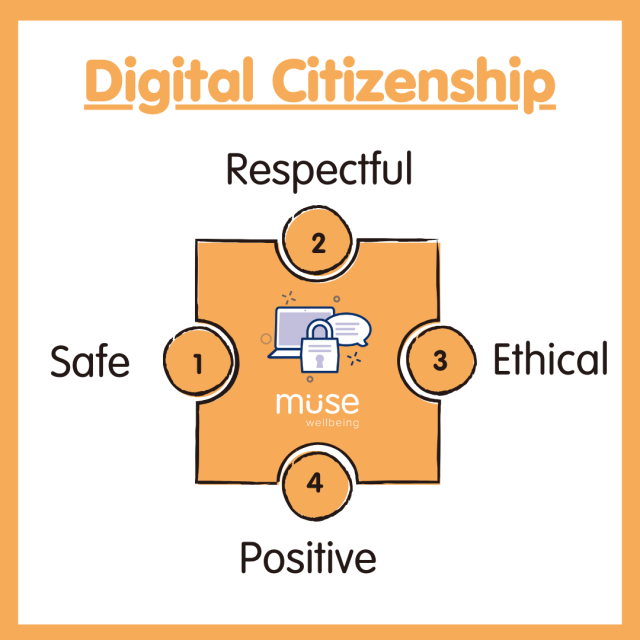
Just as schools teach children to collaborate, communicate, and discern right from wrong in the physical world, these principles must now be applied to the digital realm. Regardless of personal views on the increasing use of technology among young children, teachers have a responsibility to equip their students with the skills needed to safely and intelligently participate in online communities
Digital Citizenship Definition For Students
Providing a clear definition of digital citizenship for students will not only protect them from potential online dangers but also safeguard their future. Universities and workplaces often analyze the digital footprint of applicants to ensure they are selecting the right candidates. Teaching children from a young age that their online behavior can have long-lasting consequences will help open up numerous opportunities for them in the future.
When defining digital citizenship, it’s important to go beyond simply telling students it’s about participating safely and responsibly online. Practical explanations that children across primary school can understand are essential. This is why using a comprehensive PSHE scheme like Muse Wellbeing is beneficial. It ensures that topics like digital citizenship are introduced in Year 1 and progressively built upon through to Year 6.
Teaching Digital Citizenship in Primary Schools
Teaching digital citizenship in primary schools can be effectively integrated into a comprehensive PSHE curriculum. A PSHE curriculum provider like Muse Wellbeing equips teachers with all the necessary resources to deliver engaging and enjoyable lessons through a progressive set of learning objectives.
Although digital citizenship is not part of the mandatory RSE curriculum, it remains essential. Muse Wellbeing addresses this by including digital citizenship lessons throughout their schemes of work:
- Year 1: Simple strategies for being safe digital citizens, positive online communication, understanding cyberbullying, and knowing when to take breaks from technology.
- Year 2: Key characteristics of a good digital citizen, positive online communication, and the awareness that people may not always be who they claim to be online.
- Year 3: The impact of technology on well-being, developing a digital identity, and giving proper credit for online content.
- Year 4: The importance of strong passwords, understanding age restrictions on certain parts of the internet (such as social media and games), the creation and impact of a digital footprint on well-being and reputation, and using images and emojis for positive online communication.
- Year 5: Using technology in a balanced way to protect well-being, stopping harmful communication online, and preventing cyberbullying.
- Year 6: Understanding the risks of technology addiction and the benefits and risks associated with social media.
Why Is Digital Citizenship Important For Students?
According to a report from internetmatters.org, the biggest concern amongst parents of primary-aged children regarding internet access is the desire to give them more freedom while worrying about the potential for unintended exposure to harmful content.
Despite these concerns, the same report found that only 49% of parents with children aged 6-10 had discussed online safety with them in the past month. Given that students will access the internet regardless, schools have a growing responsibility to ensure that they do so safely, protecting both themselves and their online communities.
Incorporating digital citizenship into a school’s PSHE curriculum is essential for improving safety, preventing and managing cyberbullying, and reducing exposure to unsafe content.
How Does Digital Citizenship Affect Everyday Lives
Digital citizenship extends beyond internet safety to prepare students for an increasingly connected world. By the time students leave school, technology will likely play an even more significant role in both their professional and personal lives.
Digital citizenship equips students with the knowledge to maintain a positive digital footprint. It covers topics such as plagiarism, copyright issues, the effects of excessive screen time, the importance of digital detoxes, and balancing online activities with real-world interactions.
In today’s world, being a good digital citizen is just as crucial as being a responsible citizen in real life. Schools have always aimed to nurture independent, well-rounded young people ready to thrive after education; now, they must apply these same principles to the online world as well.
Final Thoughts: Teaching Digital Citizenship in PSHE
Learning to be a good digital citizen is quite similar to learning to be a responsible citizen in the real world; students need to be taught the appropriate and safe ways to interact online.
While it may be easy to overlook the importance of teaching digital citizenship to primary school students, it is becoming an essential part of the curriculum as many children already have access to phones and tablets when they start school.
By using Muse Wellbeing’s PSHE scheme of work, teachers can be confident that they are delivering comprehensive digital citizenship and internet safety lessons. These fully planned and resourced lessons build on students’ knowledge throughout their primary education, ensuring a thorough understanding of how to navigate the digital world safely and responsibly.
The Muse Wellbeing PSHE curriculum has been created using five core values that nurture safer learning and boost student well-being. The fifth value is digital citizenship and online safety, as the teachers, well-being advocates, and educational creatives who developed the curriculum recognize the importance of primary school children understanding digital citizenship.
Muse Wellbeing
Support
Subscribe for RSHE & Wellbeing Updates & Learning Resources
Copyright © 2025 Muse | All Rights Reserved.
Would you like to logout of Muse Wellbeing?


